The Connection Between Posture And Back Pain: What You Need To Know
Are you tired of constantly dealing with back pain? Well, it turns out that the way you carry yourself plays a significant role in how your back feels. In this article, we will explore the connection between posture and back pain, uncovering what you need to know to alleviate and prevent discomfort. So sit up straight, relax, and let’s dig into the science behind proper posture and a pain-free back.
The Importance of Good Posture
Good posture is essential for maintaining a healthy body and overall well-being. It refers to the position in which you hold your body while sitting, standing, or lying down. Having good posture allows for proper body alignment, which in turn helps distribute the weight of your body evenly. When you maintain good posture, your muscles and ligaments are able to work efficiently, reducing the strain and stress on your bones and joints. Good posture also helps optimize the functioning of your organs and promotes better breathing and circulation.
Definition of posture
Posture can be defined as the position and alignment of your body parts in relation to one another. It involves the proper positioning of the spine, as well as the balance and coordination of the muscles and ligaments that support it. Good posture is characterized by a natural and relaxed alignment of the body, with the spine maintaining its three natural curves: the inward curve at the neck (cervical curve), the outward curve at the upper back (thoracic curve), and the inward curve at the lower back (lumbar curve).
Role of posture in body alignment
Proper body alignment is crucial for maintaining good posture and overall health. When the body is properly aligned, the bones, joints, muscles, and ligaments are in their optimal positions, reducing the risk of strain, pressure, and injuries. Good posture helps minimize the stress on the various structures of the body, such as the spine, discs, and nerves, allowing them to function properly. It also helps maintain the natural curves of the spine, providing stability and flexibility to the body.
Effects of poor posture on overall health
Poor posture can have significant negative effects on your overall health. When you consistently have bad posture, it can lead to muscle imbalances, weakness, and tightness. These imbalances can cause poor movement mechanics and increase the risk of injuries. Furthermore, poor posture can lead to chronic pain, particularly in the neck, shoulders, and back. It can also affect your breathing and digestion, as it may restrict the movement and function of the organs in your chest and abdomen. Additionally, poor posture can have a negative impact on your mood and self-confidence, as it can affect your appearance and body language.
Common Causes of Poor Posture
Various factors contribute to poor posture, many of which are common in today’s modern lifestyle. Understanding these causes can help you identify potential areas for improvement and make necessary changes to improve your posture.
Sedentary lifestyle
One of the leading causes of poor posture is a sedentary lifestyle. Spending long hours sitting, whether at a desk, in front of a computer, or while driving, can lead to postural imbalances and muscle weakness. Sitting for extended periods of time can cause your muscles to become stiff and tight, particularly in the hips, lower back, and shoulders.
Improper ergonomics
Another common cause of poor posture is improper ergonomics. This refers to the design and arrangement of your work environment, such as your desk, chair, and computer setup. If your workspace is not properly aligned to your body’s needs, it can cause postural imbalances and strain on your muscles and joints. For example, if your chair doesn’t provide adequate lumbar support or your computer monitor is positioned too low, it can lead to slouching and neck strain.
Muscle imbalances and weakness
Muscle imbalances and weakness can also contribute to poor posture. Imbalances occur when certain muscles are overactive or tight, while their opposing muscles are weak or underactive. This imbalance can cause postural deviations and affect the overall alignment of your body. Weak core muscles, for example, can lead to increased strain on the lower back and contribute to a slouched posture.
Pregnancy and weight gain
Pregnancy and significant weight gain can cause postural changes due to the increased load on the body. As the abdomen grows larger, the center of gravity shifts forward, causing the spine to adapt. This can result in a swayback posture, with an exaggerated curve in the lower back. The additional weight can also put strain on the muscles and ligaments, leading to further postural imbalances.
Aging and degenerative changes
As we age, our bodies undergo natural changes, including changes in posture. Degenerative changes in the spine, such as disc degeneration and arthritis, can affect the alignment of the spine and contribute to poor posture. Muscle loss and decreased flexibility that often occur with aging can also impact posture, leading to a more rounded or stooped posture.
Understanding Back Pain
Back pain is a common complaint that can greatly impact daily life. Understanding the different types of back pain and their causes is crucial in addressing and managing this issue effectively.
Types of back pain
Back pain can be classified into two main categories: acute and chronic. Acute back pain refers to sudden and short-term episodes of pain that typically last for less than three months. Chronic back pain, on the other hand, persists for longer periods, often more than three months. It can be intermittent or constant, and its severity can vary from mild to debilitating.
Common causes of back pain
There are various factors that can contribute to back pain. Poor posture is one of the leading causes, as it puts excessive stress on the spine and surrounding structures. Other common causes include muscle strains and sprains, herniated discs, spinal stenosis, arthritis, and osteoporosis. In some cases, back pain may also be the result of underlying medical conditions or injuries, such as kidney stones or fractures.
How back pain affects daily life
Back pain can significantly impact daily life, making it difficult to perform simple tasks and engage in physical activities. The pain can limit your mobility and range of motion, making it challenging to carry out everyday activities, such as bending, lifting, or even sitting for prolonged periods. Back pain can also interfere with sleep, causing fatigue and affecting overall quality of life. Additionally, chronic back pain can lead to emotional distress, including anxiety and depression, due to the limitations it imposes on daily functioning.
The Relationship Between Posture and Back Pain
Maintaining good posture is critical for preventing and managing back pain. Understanding how posture affects spinal alignment and the mechanisms behind back pain related to posture can help motivate you to prioritize your posture.
The spine’s natural curve
The spine is naturally curved, consisting of three main sections: the cervical spine (neck), the thoracic spine (upper back), and the lumbar spine (lower back). These curves are designed to provide optimal support, stability, and shock absorption for the body. The natural curves of the spine help distribute weight evenly, reducing stress on the vertebrae, discs, and other structures.
Impact of poor posture on spinal alignment
Poor posture disrupts the natural alignment of the spine, leading to misalignments and imbalances. Slouching or hunching forward, for example, can flatten the natural curves, putting excessive strain on the discs, joints, and muscles. Conversely, an exaggerated arch in the lower back, known as hyperlordosis, can also cause problems by increasing stress on the lumbar spine and contributing to muscle imbalances.
Mechanisms of back pain related to posture
Poor posture can contribute to back pain through various mechanisms. When the spine is misaligned, it can compress the discs and irritate the nerves, leading to pain and discomfort. muscle imbalances caused by poor posture can also result in muscle tension and trigger points, further exacerbating pain. Additionally, poor posture can lead to increased strain on the supporting muscles and ligaments, causing overuse injuries and inflammation.
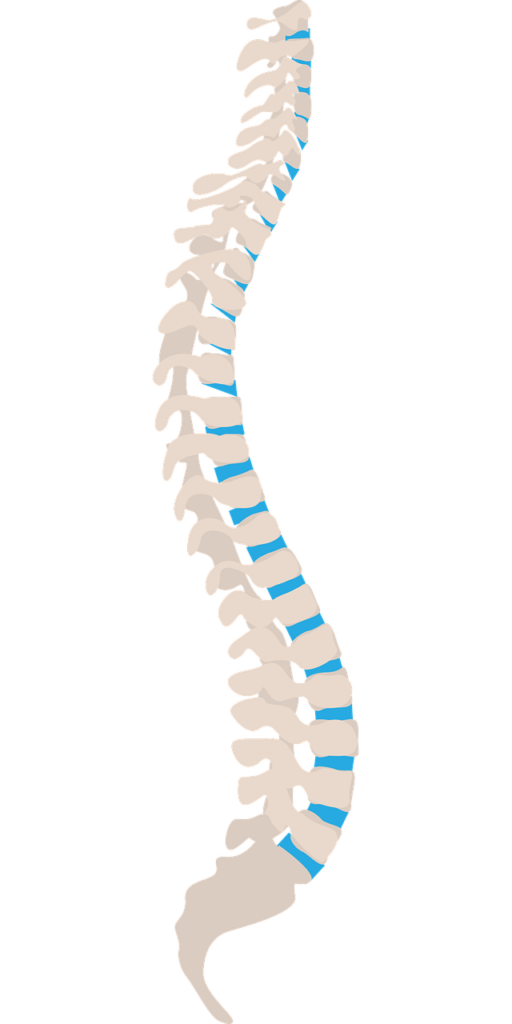
Postural Imbalances and Muscular Dysfunction
Postural imbalances and muscular dysfunction are common issues that affect many individuals who consistently have poor posture. These imbalances can lead to a variety of postural problems, often resulting in back pain.
Forward head posture
Forward head posture is a common postural problem in today’s digital age, characterized by the protrusion of the head beyond the shoulders. This posture puts excessive strain on the neck and upper back muscles, leading to muscle imbalances, tension, and neck pain.
Rounded shoulders and upper back
Rounded shoulders and an excessive curvature of the upper back, known as thoracic kyphosis, are often caused by prolonged slouching or sitting with poor posture. This postural deviation can contribute to muscle imbalances, tightness, and pain in the upper back and neck.
Excessive lordosis or swayback
Excessive lordosis, also known as swayback, refers to an exaggerated inward curve of the lower back. This postural deviation can result from weak abdominal muscles, tight hip flexors, and poor posture habits. It can lead to strain on the lumbar spine, causing lower back pain.
Flat back or posterior pelvic tilt
Flat back, or posterior pelvic tilt, occurs when the pelvis tilts backward, flattening the natural curve of the lumbar spine. This postural deviation often results from tight hip flexors and weak gluteal muscles, contributing to lower back pain and hip discomfort.
Uneven hips
Uneven hips, also called leg length discrepancy, occur when one leg is shorter than the other. This can lead to postural imbalances, with one side of the body compensating for the height difference. As a result, it can cause lower back pain, hip pain, and muscular imbalances.

Muscle imbalances and compensation patterns
Muscle imbalances and compensation patterns often develop as a result of poor posture. When certain muscles become overactive or tight, they can pull the body out of alignment, causing compensatory movements and imbalances in other muscle groups. These imbalances and compensations can lead to pain and dysfunction throughout the body.
Specific Postural Problems and Back Pain
Certain postural problems are commonly associated with back pain. Understanding these specific conditions can help you identify potential issues and seek appropriate treatment and interventions.
Hunchback or kyphosis
Hunchback, also known as kyphosis, refers to an exaggerated rounding of the upper back, typically in the thoracic spine. It can be caused by poor posture, osteoporosis, spinal fractures, or other medical conditions. Kyphosis can lead to back pain, difficulty breathing, and limited mobility.
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a condition characterized by an abnormal sideways curvature of the spine. It can be congenital (present at birth) or develop during childhood or adolescence. Scoliosis can cause back pain, muscle imbalances, and postural deviations. Treatment may involve bracing, physical therapy, or, in severe cases, surgery.
Military or sway back posture
A military or sway back posture is characterized by an exaggerated arch in the lower back. It can result from muscle imbalances, weak core muscles, or poor posture habits. This posture can cause lower back pain and contribute to other postural problems.
Anterior pelvic tilt
Anterior pelvic tilt is a postural misalignment characterized by a forward tilting of the pelvis. This posture can result from tight hip flexors and weak gluteal muscles. Anterior pelvic tilt can cause lower back pain and contribute to hip and knee discomfort.

Postural assessments and their role in diagnosing back pain
Postural assessments play an important role in diagnosing back pain and identifying underlying postural imbalances. These assessments involve observing and evaluating an individual’s posture from different angles and assessing the alignment of various body parts. Postural assessments help healthcare professionals identify any deviations or imbalances, which can guide appropriate treatment and interventions.
Preventing and Treating Back Pain Through Postural Corrections
Preventing and treating back pain through postural corrections involves a multifaceted approach that includes lifestyle modifications, exercises, and professional guidance. By addressing postural imbalances and making the necessary corrections, you can significantly reduce the risk of back pain and improve overall well-being.
Strengthening exercises for the core and back muscles
Strengthening exercises for the core and back muscles are crucial for maintaining proper posture and preventing back pain. These exercises focus on strengthening the muscles that support the spine, such as the abdominals, back extensors, and gluteal muscles. Examples of such exercises include planks, bridges, and bird dogs.
Improving flexibility and mobility
Improving flexibility and mobility is essential for maintaining good posture and preventing back pain. Stretching exercises that target tight muscles, such as the chest, hip flexors, and hamstrings, can help improve posture and reduce strain on the back. Incorporating activities like yoga or Pilates can also help improve flexibility, posture, and body awareness.
Ergonomic adjustments in the workplace
Making ergonomic adjustments in the workplace can significantly improve posture and reduce the risk of back pain. This includes setting up a workstation that promotes proper body alignment, such as using an ergonomic chair, adjusting desk height, and positioning the computer monitor at eye level. Taking frequent breaks to stretch and move around can also help alleviate postural stress.
Proper lifting and carrying techniques
Practicing proper lifting and carrying techniques is essential for preventing back injuries and maintaining good posture. When lifting heavy objects, it is important to bend at the knees, engage the core muscles, and lift with the legs rather than the back. Avoiding twisting motions and distributing the load evenly can also help reduce the strain on the back.
The role of physical therapy in postural corrections
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in postural corrections and back pain management. A physical therapist can assess your posture, identify any imbalances, and develop an individualized treatment plan to address those issues. Physical therapy may involve a combination of manual therapy, exercises, and education on proper body mechanics and posture.
Postural Awareness and Behavioral Changes
Developing postural awareness and making behavioral changes are essential steps in improving posture and preventing back pain. By being mindful of your posture throughout the day and implementing healthy habits and postural cues, you can make a significant difference in your overall posture and well-being.
The importance of mindfulness
Mindfulness plays a key role in maintaining good posture. By being aware of your body and its alignment, you can catch yourself when you start to slouch or adopt poor posture habits. Mindfulness also helps you recognize the effects of poor posture on your body and motivates you to make the necessary changes.
Developing healthy habits and postural cues
Developing healthy habits and postural cues can help reinforce good posture. Setting reminders or cues throughout the day to check and correct your posture can be helpful. Establishing a routine of regular breaks to stretch and move around can also aid in maintaining good posture and preventing postural fatigue.
The role of yoga and Pilates in improving posture
Yoga and Pilates are excellent forms of exercise that can help improve posture, flexibility, and body awareness. These practices emphasize proper body alignment and utilize various exercises and stretches to strengthen the muscles that support good posture. The mind-body connection cultivated in yoga and Pilates can also enhance postural awareness and mindfulness.
Incorporating movement breaks and regular exercise
Incorporating movement breaks and regular exercise into your daily routine is crucial for maintaining good posture and overall health. Taking short breaks to stand up, stretch, and move around can help alleviate postural stress and prevent the negative effects of prolonged sitting. Engaging in regular exercise, such as walking, swimming, or strength training, can also help strengthen muscles and improve posture.
Tips for maintaining good posture throughout the day
Maintaining good posture throughout the day requires conscious effort and practice. Here are some tips to help you maintain good posture:
- Sit up straight and avoid slouching when sitting or standing.
- Keep your shoulders relaxed and rolled back, avoiding rounding or hunching.
- Engage your core muscles to support your spine and maintain proper alignment.
- Keep your feet flat on the ground when sitting or standing, with your weight evenly distributed.
- Use supportive pillows and cushions when sitting or lying down to maintain proper spinal alignment.
- Avoid crossing your legs for extended periods, as this can lead to postural imbalances.
- Take regular breaks to stretch and move around, especially during long periods of sitting.
- Maintain a balanced exercise routine, incorporating both cardiovascular exercises and strength training to support good posture.
- Pay attention to your body’s cues and make adjustments as needed to maintain proper alignment and relieve tension.
- Consider seeking professional help from healthcare providers, such as chiropractors or physical therapists, for guidance and support in improving your posture.
Evaluating Your Posture and Seeking Professional Help
Evaluating your posture and seeking professional help, when necessary, are important steps in improving your posture and managing back pain.
Self-assessment of posture
You can perform a self-assessment of your posture by observing your alignment in a mirror or having someone take pictures of you from different angles. Pay attention to the position of your head, shoulders, spine, hips, and feet. Compare your posture to the ideal alignment, considering the natural curves of your spine.
When to consult a healthcare professional
If you are experiencing chronic back pain or have concerns about your posture, it may be beneficial to consult a healthcare professional. They can perform a thorough evaluation of your posture, identify any underlying issues, and develop a personalized treatment plan to address your specific needs. In some cases, an interdisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals from different specialties, such as chiropractors, physical therapists, or orthopedic specialists, may be necessary.
The role of chiropractors, physical therapists, and other specialists
Chiropractors, physical therapists, and other specialists play a vital role in diagnosing, treating, and managing back pain and postural imbalances. Chiropractors are trained in evaluating and correcting spinal misalignments, while physical therapists specialize in rehabilitating and correcting musculoskeletal imbalances through targeted exercises and therapies. Other specialists, such as orthopedic surgeons or pain management specialists, may be involved in cases where more invasive interventions or medical treatments are necessary.
Conclusion
The significance of good posture in preventing and managing back pain cannot be overstated. By maintaining good posture, you can reduce the risk of postural imbalances, alleviate muscle tension, and optimize the functioning of your spine and supporting structures. Empowering individuals to take control of their posture, make necessary postural corrections, and prioritize their overall well-being is crucial in promoting a holistic approach to back pain management. By incorporating proper ergonomics, regular exercise, and postural awareness into your daily life, you can significantly improve your posture, reduce the risk of back pain, and enhance your overall quality of life.




